Simulating the perturbational complexity index at the edge of chaos
Many objective measures of consciousness have been proposed, but the perturbational complexity index (PCI) has proven uniquely reliable within subjects and across levels of consciousness. Meanwhile, prior work with reservoir networks shows that to exhibit sophisticated information processing capabilities, network dynamics should stay close to a boundary between order and chaos. Mounting evidence is also showing that conscious cortical electrodynamics are poised near such a boundary, but there is no work examining PCI in this context. In this study, we built a binary reservoir network to investigate whether PCI also peaks near a corresponding boundary (called a critical point). We found that PCI exhibits an inverse U-shaped relationship with chaoticity, with values maximal when network dynamics are situated near this critical point, and we present possible explanations for these findings in the context of how PCI is operationalized. Contrary to related work, however, we also found that Lempel-Ziv complexity (LZc) does not exhibit an inverse U-shaped relationship nor peak near a corresponding critical point. We suggest that LZc alone may misrepresent the degree to which a system’s activation dynamics correspond with those of a conscious brain. We conclude with a discussion of limitations of this study and opportunities for future work, such as employing alternative computational techniques and replicating the study in models that are more neurally representative.
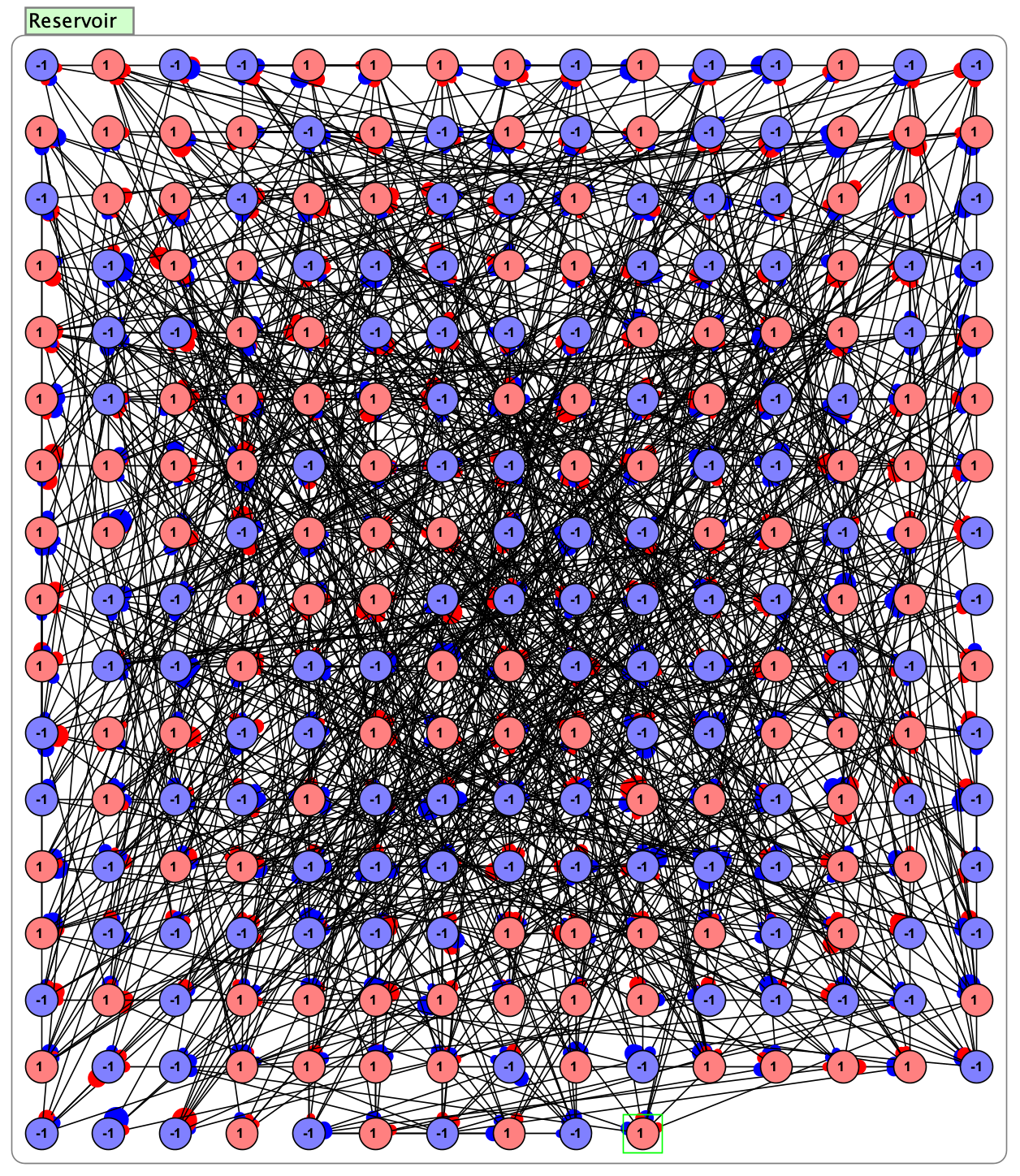
Figure 1. Diagram of the binary reservoir model in Simbrain. Model parameters were based on Bertschinger, N., Natschläger, T., & Legenstein, R. (2004).

Figure 2. Individual un-normalized results for the perturbational complexity index (PCI), Lempel-Ziv complexity (LZc), and the largest Lyapunov exponent (LLE), from periodic to chaotic network dynamics in the binary reservoir model. The mean connection-weight variance that corresponded with the critical point is indicated by the red vertical line in all three plots. From left to right: (A) PCI appeared to peak near the critical point and on the chaotic side, and a clear inverse U-shaped relationship was observed qualitatively. (B) Lempel-Ziv complexity did not appear to peak near the critical point, and no inverse U-shaped relationship was observed qualitatively. (C) The 21 median largest Lyapunov exponents show qualitatively which was nearest to zero and thus which mean connection-weight variance corresponded with the critical point.
Talks: University of California, Merced, Department of Cognitive and Information Sciences Annual Project Mini-Conference, Merced, CA (May 9th, 2022)
